|
|
The trilogy's plot is based upon al-Qaeda's obtaining old Soviet gun-type test devices. This source was chosen for two reasons: to avoid the trap of having to go into excruciating detail about the bomb design, perhaps revealing too much information; and to include some history of the America’s Manhattan Project and the Soviet’s First Main Directorate. The history of nuclear fission and the atomic bomb began in the fall of 1938 with the splitting of the first uranium atom at the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute in Berlin, Germany. Soon scientists around the world were adding their discoveries to the rapidly growing body of information. Nuclear fission dangled the promise of a new energy source greater than any known to date. To countries such as Germany—then Nazi Germany ruled by Adolph Hitler—it held the promise of becoming a mighty weapon. Word of the potential danger of an “Atomic Bomb” arrived in America with scientists fleeing Hitler’s “New Order.” Among them were three refugee Hungarian scientists: Leo Szilart, Eugene Wigner, and Edward Teller. Together they were able to convince Albert Einstein of the danger of a Hitler Atomic Bomb. Albert Einstein wrote his famous “dangers of uranium fission letter” to President Roosevelt. President Roosevelt ordered the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD) to investigate atomic energy. OSRD formed an Atomic Committee, code name “S-1.” The S-1 committee identified five methods of producing uranium-235 and plutonium-239 and recommended all five methods be placed into production. The president quickly returned it with “OK, FDR” written in one corner. Thus began the greatest scientific, engineering, and manufacturing effort in the history of mankind. The Corps of Engineers was given the task of building the facilities, named The Manhattan Project. On September 23, 1942 newly promoted Brigadier General Leslie Groves officially took charge of the Manhattan Project. Under Groves’ leadership, the Manhattan Project encompassed responsibility for all science, engineering, construction and operation of production facilities required to deliver the atomic bomb. During the next two years, land was acquired and three new cities built to provide housing for personnel needed to construct and operate the massive facilities required for production of atomic bombs. These facilities included: Oak Ridge, Tennessee, encompassing fifty-four thousand acres, for uranium separation; Los Alamos, New Mexico, located in a high valley called a “mesa” surrounded by mountains, for a bomb design laboratory; and Hanford, Washington, six hundred square miles, for plutonium production. General Groves built production facilities for technologies not yet developed—using components not yet invented; marshaled the resources of major universities; obtained the assistance and support of America’s greatest corporations—many of which placed the future of their companies at risk for the project; and gathered the greatest group of scientists, engineers and inventors ever assembled. Uranium-235 and plutonium-239, required to build The Bomb, possess different atomic, physical and chemical properties. The Project’s scientists ultimately determined that uranium-235 would be used to build a gun-type atomic bomb—two subcritical components would form a supercritical mass when one was shot down a cannon barrel into the other. Much less plutonium-239 was required to form a supercritical mass. Thus, plutonium-239 would be used as the fissile material for the implosion bomb. American leadership, ingenuity and determination prevailed. Technical problems were solved—many at the last minute. |
||
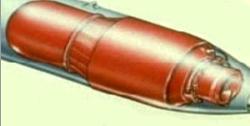
First Atomic Bombs Little Boy and Fat Man |
||
 |
||||
The Bomb project finally came together in early 1945 when Oak Ridge produced enough uranium-235 for one gun-type bomb—The Little Boy—and enough plutonium-239 for two implosion bombs—Gadget and Fat Man. What is the difference between a gun-type and implosion nuclear weapon? Click Here |
||||
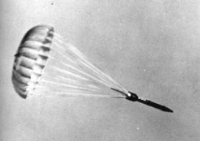
First Nuclear Detonation - 16 July 1945 |
||
 |
||||||||
Gadget, a test device, was detonated in secrecy on top of a tower at 5:29:45 a.m. mountain wartime, on July 16, 1945, at Trinity Site in the Alamogordo Test Range, New Mexico. |
||||||||
 |
||||||||
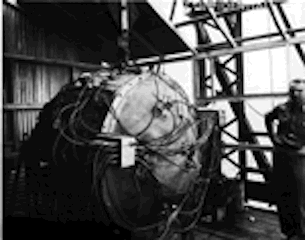
In the story, the terrorists use gun-type atomic devices. The story and technology in The Rings of Allah is based on the Little Boy, an untested gun-type bomb, the type of bomb terrorists can make if they acquire or are given enough highly enriched uranium-235. See photos of the Little Boy below. |
||||||||
 |
||||||
 |
||||||
 |
||||||
Additional photos of the Little Boy and Fat Man, including assembly and loading on B29s |
||
 |
||||
 |
||||
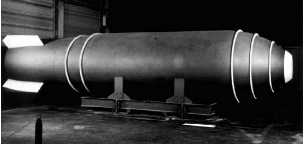
The U.S. dropped the Little Boy on Hiroshima at 8:16 a.m. on August 6, 1945, and the world officially entered the nuclear age. The 12-17 KT detonation, and its aftermath are shown above. Because Japanese leaders refused to acknowledge that Hiroshima had been destroyed by a weapon, the Fat Man was dropped on Nagasaki at 11:02 a.m., the morning of August 9, 1945, ending World War II. Usama bin Laden has said he wants to kill 4 million American men, women, and children. Technology has advanced, and a simple gun-type device the size of the Little Boy can reach yields of 50 KT—more than enough to destroy the heart of a major city, achieving bin Laden's goal. What are more modern weapons like? Technology has advanced on an exponential scale, increasing at an unbelievable pace. By the mid 1960's implosion weapons had advanced in both size and yield. Some grew to the huge Mk-17 and MK 41 thermonuclear bombs with megaton (MT) yields—yields beyond human comprehension. The MK-41, with a yield of 24 MT, was the highest-yield bomb stockpiled by the U.S. The MK-17 was physically the largest.
The big boys. |
||
 |
||||
 |
||||
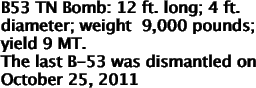 |
||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Early Soviet Nuclear Weapons mentioned in The Rings of Allah and Behold, an Ashen Horse. |
||
 |
||||
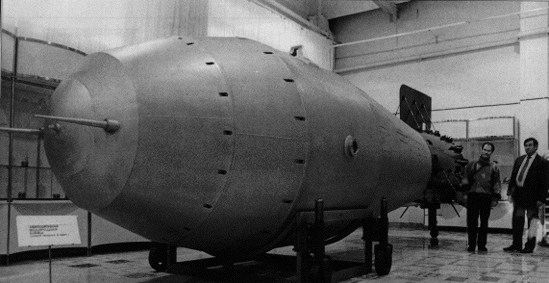 |
||||
Tsar Bomba, the largest, three stage thermonuclear bomb ever built. Itwas tested on October 30, 1961. It weighed 25 tons. Designed to be 100 MT, the tested bomb was reported to be 52 MT. |
||||
From right to left: Joe-1 (First Lightning, 22 KT), Joe-3 (38 KT), and Joe-4 (400 KT). |
||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||